What materials are LED electronic candles made of and are they fire-resistant?
General Composition of LED Electronic Candles
LED electronic candles are designed to replicate the look and feel of traditional wax candles while eliminating the risks associated with open flames. These products typically combine several materials, including plastics, wax-like coatings, electronic components, and light-emitting diodes. The main goal in their design is to create a safe, reusable, and aesthetically pleasing product that can be used in homes, events, or public spaces without the hazards of fire or dripping wax. Each component serves a particular purpose, from the outer shell for appearance to the electronic core that powers the LED light source.
Outer Shell Materials
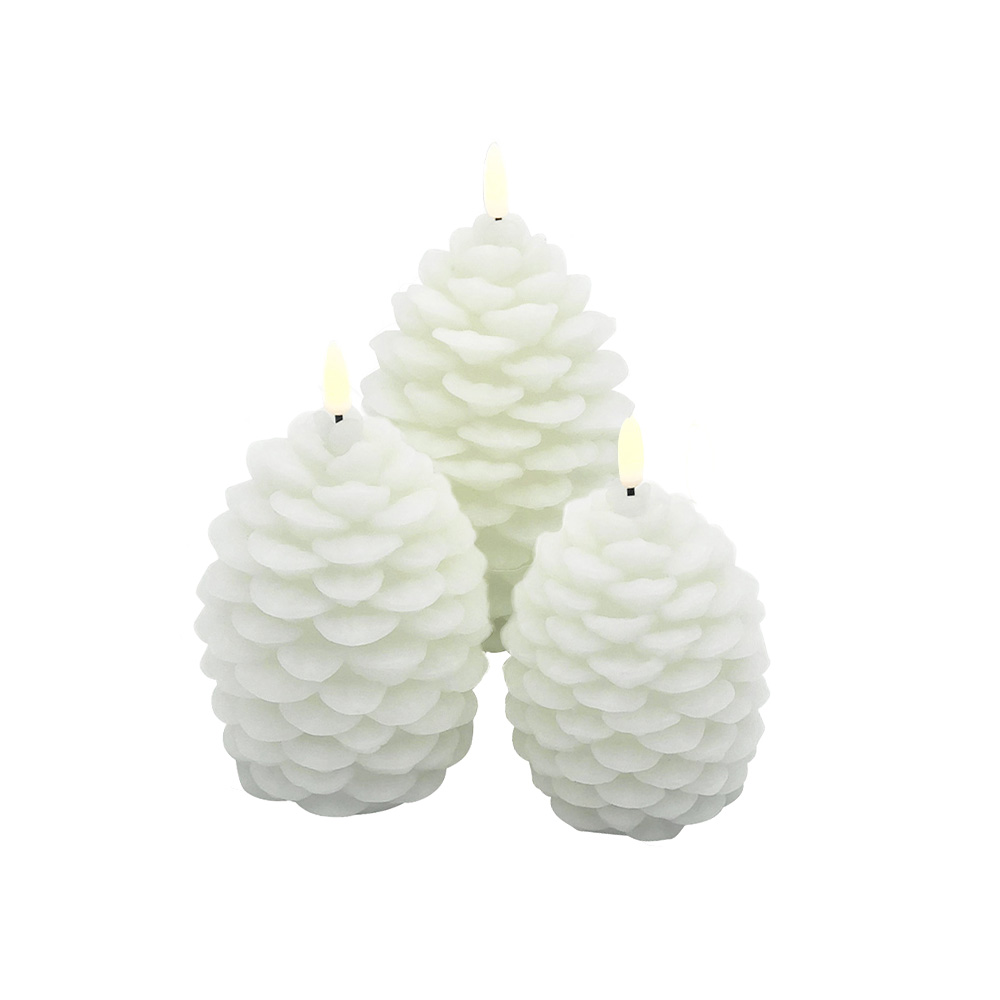
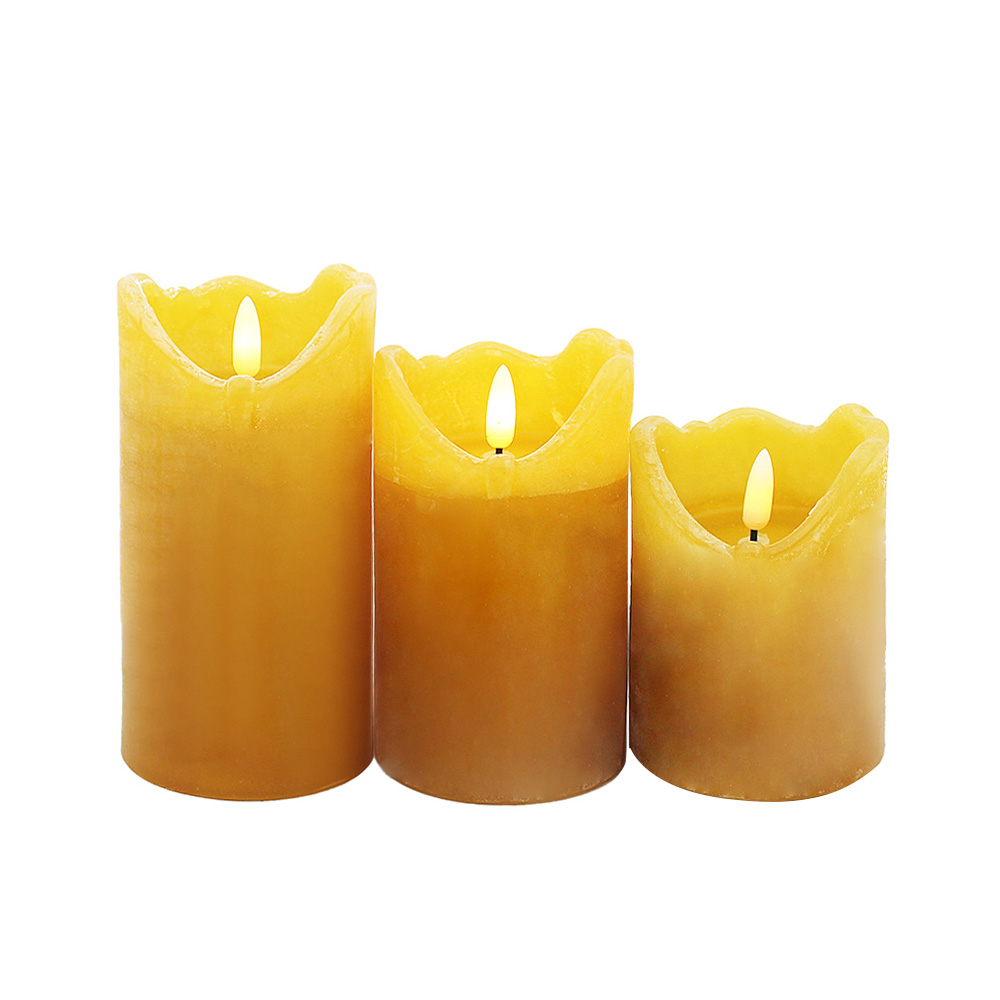
The outer shell of an LED electronic candle is usually made from durable plastic or real paraffin wax, depending on the design and intended market. Plastic shells are popular for long-lasting, lightweight, and cost-effective models. They are often crafted from ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) or PP (Polypropylene), both of which are commonly used in household appliances and consumer products. On the other hand, higher-end models use actual paraffin wax on the outer layer to mimic the look of a real candle more closely. This gives a more authentic aesthetic, though paraffin wax itself is not inherently fire-resistant, which makes the LED design safer by eliminating direct combustion.
Electronic Components and Circuitry
Inside the LED electronic candle lies the circuitry responsible for producing light and controlling additional features such as flickering effects, timers, or remote operation. The circuit board is typically made from fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin, also known as FR4, which provides strength, insulation, and moderate heat resistance. Electrical connections are usually copper-based, ensuring conductivity while maintaining durability. Batteries, most often AA, AAA, or button cell types, power the light source. These electronic components are carefully arranged to avoid overheating and to prolong the overall life of the product.
Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
The LED is the core element of electronic candles, producing illumination in different shades such as warm yellow, white, or multicolor variations. LEDs are semiconductor-based devices made from materials such as gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide, or gallium nitride, depending on the color output. These materials are chosen for their ability to emit light efficiently while generating very little heat compared to incandescent bulbs. Their durability, low energy consumption, and long lifespan make LEDs a reliable choice for products designed to simulate candlelight safely.
Wax-like Coatings and Decorative Finishes
Many LED electronic candles include wax-like coatings or decorative finishes to enhance realism. Real paraffin wax is often layered on the outer shell to provide texture and a familiar candle-like surface. Some manufacturers use synthetic coatings, such as silicone-based or resin materials, to imitate wax while improving durability and preventing chipping. These coatings are not meant to burn, as the product does not rely on combustion, but they enhance the tactile and visual similarity to traditional candles.
Base and Housing Materials
The base of an LED candle, which houses the batteries and sometimes the switch, is usually made from ABS plastic. This material is chosen because it is strong, resistant to impact, and capable of tolerating moderate heat. In some cases, the base may also incorporate metal elements, such as stainless steel or aluminum, for durability and stability. These materials help maintain the overall structure of the candle while allowing easy access for battery replacement and ensuring safe operation.
Fire-Resistance Characteristics
LED electronic candles are designed to be far safer than real candles because they do not rely on flame. Plastics such as ABS and PP are moderately fire-resistant, with ABS being particularly valued for its flame-retardant properties when treated with additives. Paraffin wax, while combustible in natural form, is safe in this context because the candle does not generate an open flame or high heat. The LED itself produces minimal heat, and the surrounding materials are chosen to prevent ignition even in prolonged use. In comparison to traditional candles, the fire risk of LED versions is extremely low.
| Material | Function | Fire-Resistance Level |
|---|---|---|
| ABS Plastic | Outer shell, base housing | Moderate, often flame-retardant |
| Paraffin Wax | Realistic outer layer | Low, combustible but safe without flame |
| FR4 (Fiberglass Epoxy) | Circuit board substrate | High, good insulation and heat resistance |
| LED Semiconductor | Light source | High, produces negligible heat |
Battery Safety Considerations
Batteries are an important component of LED candles, and their safety is crucial in determining whether the product as a whole can be considered fire-resistant. Common alkaline batteries or rechargeable lithium-ion cells are generally safe when used correctly, though overheating or leakage may occur in poor-quality products. To mitigate risks, manufacturers design battery compartments with proper insulation and sometimes include safety circuits to prevent overcharging or short circuits. Unlike open-flame candles, where the primary risk is ignition, LED candles mainly require monitoring of battery quality and usage.
Durability in Heat Exposure
Although LED candles are designed to be safe, their materials do have limits in terms of heat resistance. ABS plastic, for example, can deform if exposed to very high temperatures above 100°C. Paraffin wax may soften in warm conditions, though this does not pose a fire hazard in the absence of flame. LED components remain cool, but the overall candle should not be left in direct sunlight or near heaters for extended periods. Compared to ordinary candles, however, the risk of fire-related accidents is dramatically reduced because no ignition source exists within the product.
Comparison with Traditional Candles
When evaluating fire resistance, the difference between LED electronic candles and traditional wax candles is clear. A traditional candle relies on an open flame, making it inherently combustible and potentially dangerous if left unattended. LED candles, by contrast, use materials that may not be entirely flameproof in raw form, but their design eliminates open fire, making them much safer in practical use. They can be left on overnight, used near fabrics, or placed in decorative arrangements without the same risks that accompany real flame.
| Feature | LED Electronic Candle | Traditional Candle |
|---|---|---|
| Light Source | LED, no flame | Burning wick with flame |
| Outer Material | Plastic or paraffin wax | Paraffin or beeswax |
| Fire Risk | Very low, no ignition source | High, open flame |
| Heat Production | Minimal | High |
Environmental and Safety Regulations
LED electronic candles are often produced according to international safety and environmental standards, such as RoHS compliance, which restricts the use of hazardous substances in electronic components. Many models also undergo fire safety testing to ensure that their plastic casings resist ignition under standard conditions. These regulations guarantee that the materials used, including ABS plastics and electronic parts, meet acceptable fire-resistance benchmarks. While traditional candles cannot escape the inherent risks of fire, LED models are specifically engineered to align with modern safety expectations.
Long-Term Reliability of Materials
Over time, the materials used in LED candles must withstand repeated use, battery changes, and exposure to indoor conditions. ABS plastic maintains structural strength, while paraffin coatings may show wear but remain stable in typical environments. The LED itself has an exceptionally long operational life, often rated for tens of thousands of hours, meaning that the light source does not degrade quickly. The fire-resistant properties of the materials ensure that the candle remains a safe household accessory throughout its lifespan, provided it is used under recommended conditions.
Applications in Different Settings
Because of their materials and fire-resistant design, LED electronic candles are suitable for a variety of settings. They can be safely used in homes with children or pets, in hotels where open flames are prohibited, and at public events where safety regulations restrict real candles. Their construction materials balance realism with durability, ensuring that they function well across environments while minimizing risks. Ordinary candles, though traditional, cannot provide the same level of assurance in restricted or sensitive locations, making LED candles a more versatile option.

Ningbo Weizhi Electronics Co., Ltd.
- We will be pleased to provide products with high quality, reasonable price, punctual delivery and best service for you!
GET A QUOTE
Building 2, No. 2477, Cihai North Road, Xipu Town, Zhenhai District, Ningbo City, China
-
 +86-18067520996
+86-18067520996
-
 +86-574-86561907
+86-574-86561907
-
 +86-574-86561907
+86-574-86561907
-
 [email protected]
[email protected]
- +8618067520996
- +86 18074202116
Copyright 2024 Ningbo Weizhi Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.




 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch